
It is trusted by top Hospitals for the Prenatal Care. Note, deceleration of more than 5 minutes with reduced variability and bradycardia often means acute fetal hypoxia.SweetieSong 2.5mhz Pocket Fetal Doppler (100S5) detect baby's heart beat from 12-14 weeks of Pregnancy until giving birth.
 Prolonged decelerations last for longer than 3 minutes. Variable decelerations vary in shape and size, and are also related to contractions. They exhibit good variability and recover rapidly to the baseline rate. Variable decelerations constitute a rapid drop (reaching their lowest point less than 30 seconds after starting). They tend to coincide with uterine contractions, and might be produced by compression of your fetus’ head rather than hypoxia. The monitor can show if your heart medicine is controlling your heartbeat as it should. You start new heart medicines: These heart medicines may be used to make your heartbeat faster or slower. Many parents opt for high-tech, wearable monitors to make sure their LO’s vitals are normal, especially overnight. Fetal dopplers track heartbeat while Baby is in utero, but even after they’re born, you may want to continue tracking their heart rate and oxygen levels in those first few months. Devoe LD Antepartum fetal heart rate testing in preterm pregnancy. Baby heart rate monitors vs fetal heart dopplers. You may also need to wear it during pregnancy if you have heart disease. Early in gestation the fetal heart rate is predominately under the control of the. Early decelerations are short and shallow, with normal variability. You may need to wear a Holter monitor if you have strong, pounding heartbeats. It means your fetus is neurologically responsive and doesn’t have an oxygen deficiency.ĭecelerations represent a decrease in FHR of more than 15 bpm in bandwidth amplitude. (They start and reach maximum value in less than 30 seconds.) Accelerations last from 15 seconds to 10 minutes, and the majority occur in conjunction with fetal movements. Since it’s difficult to visually interpret this parameter, in borderline scenarios, your doctor must carefully reevaluate the results.Īccelerations represent a sudden increase in FHR of more than 15 bpm in bandwidth amplitude.
Prolonged decelerations last for longer than 3 minutes. Variable decelerations vary in shape and size, and are also related to contractions. They exhibit good variability and recover rapidly to the baseline rate. Variable decelerations constitute a rapid drop (reaching their lowest point less than 30 seconds after starting). They tend to coincide with uterine contractions, and might be produced by compression of your fetus’ head rather than hypoxia. The monitor can show if your heart medicine is controlling your heartbeat as it should. You start new heart medicines: These heart medicines may be used to make your heartbeat faster or slower. Many parents opt for high-tech, wearable monitors to make sure their LO’s vitals are normal, especially overnight. Fetal dopplers track heartbeat while Baby is in utero, but even after they’re born, you may want to continue tracking their heart rate and oxygen levels in those first few months. Devoe LD Antepartum fetal heart rate testing in preterm pregnancy. Baby heart rate monitors vs fetal heart dopplers. You may also need to wear it during pregnancy if you have heart disease. Early in gestation the fetal heart rate is predominately under the control of the. Early decelerations are short and shallow, with normal variability. You may need to wear a Holter monitor if you have strong, pounding heartbeats. It means your fetus is neurologically responsive and doesn’t have an oxygen deficiency.ĭecelerations represent a decrease in FHR of more than 15 bpm in bandwidth amplitude. (They start and reach maximum value in less than 30 seconds.) Accelerations last from 15 seconds to 10 minutes, and the majority occur in conjunction with fetal movements. Since it’s difficult to visually interpret this parameter, in borderline scenarios, your doctor must carefully reevaluate the results.Īccelerations represent a sudden increase in FHR of more than 15 bpm in bandwidth amplitude.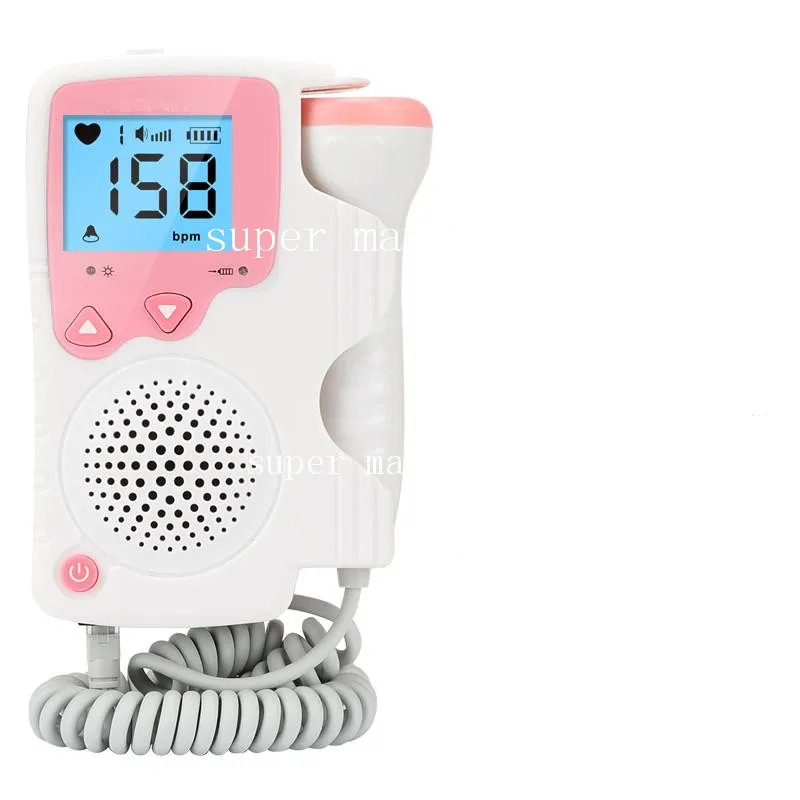 
When this variability presents itself in a fetal heart tracing, it could be caused by hypoxia of your fetus’ central nervous system. Reduced variability is a bandwidth value below 5 bpm lasting for more than 50 minutes.Increased variability is a bandwidth value exceeding 25 bpm that lasts for more than half an hour.
 Normal variability is a bandwidth value from 5 to 25 bpm. Variability describes fluctuations in the baseline FHR, whether in terms of frequency, amplitude, or magnitude. Bradycardia, in contrast, is when the fetal heart rate baseline falls below 110 bpm. Your obstetrician reviews the fetal heart tracing at regular time intervals. You have to lie down or sit in a reclined position for the test, which lasts about 20 minutes.
Normal variability is a bandwidth value from 5 to 25 bpm. Variability describes fluctuations in the baseline FHR, whether in terms of frequency, amplitude, or magnitude. Bradycardia, in contrast, is when the fetal heart rate baseline falls below 110 bpm. Your obstetrician reviews the fetal heart tracing at regular time intervals. You have to lie down or sit in a reclined position for the test, which lasts about 20 minutes. 
Electronic fetal monitoring is performed in a hospital or doctor’s office. Tachycardia occurs when the fetal heart rate baseline is above 160 bpm. The resulting printout is known as a fetal heart tracing, which will be read and analyzed.A normal baseline rate ranges from 110 to 160 bpm. These segments help establish an estimated baseline (for a duration of 10 minutes) which is expressed in beats per minute. Your doctor analyzes FHR by examining a fetal heart tracing according to baseline, variability, accelerations, and decelerations.īaseline is calculated as a mean of FHR segments that are the most horizontal, and also fluctuate the least.








 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
